BRAKING SYSTEM
INTRODUCTION:
Braking is the mechanism in the motor vehicle which is used to slowing down and stopping the vehicle to rest in the shortest possible distance. Principle of Braking system: While operating the braking system the KINETIC ENERGY of moving vehicle is converted in to HEAT ENERGY.
Functions of Brakes: Brakes have the following functions.
1.It is used to stop the vehicle.
2.It is used to control the speed where and when required.
3.It is used to control the vehicle while descending along the slope.
4.To park the vehicle and held it in stationary position without the presence of
Driver.
Requirements of Automobile Brakes:
1.It should work efficiently irrespective of road condition and quality.
2.The retardation must be uniform throughout its application.
3.The pedal effort must be within the convenient capacity of the driver.
4.It must be reliable and should not be effected by heat water and dust.
5.It should be in minimum weight.
6.It should have long life.
7.It should be easy to maintain and adjust.
8.Noise and vibrations are to be minimum.
9.There should be provision for secondary brake or parking brake.
Stopping distance and Braking efficiency:
For practical measure for braking efficiency that of the minimum
distance in which it can be brought in to rest after the brake is applied.
The stopping distance depends upon
1.Grip between the tyre and road surface.
2.Tyre tread condition.
3.Tyre inflation.
4.Nature of road surface.
The stopping distance is calculated by
D=kv2
Where d=stopping distance in kilometers.
K=Constant depending upon the road and tyre inflation.
V=velocity of the vehicle per hour.
The value of k is 1/25 for 4 wheel braking system.
1/12 for 2 wheel braking system.
The braking efficiency is calculated by the equation:
η=V
2
/3D where v=velocity of the vehicle
d=stopping distance.
Condition of Brake Braking efficiency in %
1.Perfect 90%
2.Excellent 77%
3.Good 70%
4.Fair 60%
5.Poor 50%
6.Bad 37%
7.Very bad 30%
Below Fair is very danger.
Classification of Brakes: The following are the classifications of Brakes:
1.By method of power
a) Mechanical brakes
b) Hydraulic brakes
c) Vacuum brakes
d) Air brakes
e) Electrical brakes
f) Magnetic brakes
g) Air assisted hydraulic brakes
2.By method of application:
a) Service or foot brakes
b)Parking or hand brakes
3.By method of operation:
a) Manual
b) Servo
c) Power operation
4. By method of Braking contact
a. Internal Expanding Brakes
b. External Contracting Brakes.
5. By Method of Applying Brake force:
a. Single Acting Brakes.
b. Double Acting Brakes.
Types of Mechanical Brakes:
a. Drum Brakes (Internal Expanding or External Contracting)
b. Disc Brakes (Single or Two caliper)
Drum Brakes:
Construction: The main components of drum brakes are
1. Brake drum
2. Back plate
3. Brake shoes
4. Brake Liners
5. Retaining Springs
6. Cam
7. Brake Linkages
2. Disc brakes:
There are two types of disc brakes:
1. Spot Type
a. Swinging Caliper Type
b. Sliding caliper type
2. Clutch Type
Construction: The main components of the system is
1. Master Cylinder 2. Wheel Cylinder
Advantages:
1. This system used in heavy vehicles because they are more powerful
than hydraulic or mechanical brakes.
2. It simplifies the chassis design
3. The compressed air is used for purposes like tyre inflation; for horn,
windscreen wiper etc.
Disadvantage:
If there is any leakage in passage the entire system will be fail.
Therefore sealing of air is very difficult.
keywords: illinois asbestos attorney, alabama lawyer mesothelioma, mesothelioma attorney, asbestos lawyer, mesothelioma lawyers, asbestos attorney, mesothelioma lawyer, asbestos cancer attorney, texas asbestos lawyer, illinois mesothelioma lawyer, mesothelioma attorneys, mesothelioma litigation, mesothelioma attorney texas, mesothelioma attorney houston, illinois mesothelioma attorney, texas mesothelioma attorney, new york mesothelioma lawyers, minnesota mesothelioma lawyer, atlanta asbestos attorneys, new york mesothelioma attorneys, pennsylvania mesothelioma lawyers, phoenix dui attorney, dui attorney phoenix, arizona dui attorneys, dui lawyer arizona, phoenix dui lawyers, dui attorney arizona, phoenix arizona dui lawyer, arizona dui attorney, arizona dwi attorney, phoenix dui lawyer, arizona dui lawyer, dui lawyer phoenix, arizona dui lawyers, dui lawyer scottsdale, scottsdale dui attorney, dui attorneys arizona, tempe dui lawyer, az dui attorney, dui attorney scottsdale, automobile, mechanical engineering, autocad training,auto insurance, car insurance, car insurance quote, insurance quotes, low cost insurance, cheap insurance, cheap car insurance, cheap auto insurance, car cheapest insurance, car insurance quotes, automobile insurance, auto insurance quote, cheap car insurance quote, discount auto insurance, car insurance online, insurance rates, car insurance online quote, cheapest car insurance, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet
INTRODUCTION:
Braking is the mechanism in the motor vehicle which is used to slowing down and stopping the vehicle to rest in the shortest possible distance. Principle of Braking system: While operating the braking system the KINETIC ENERGY of moving vehicle is converted in to HEAT ENERGY.
Functions of Brakes: Brakes have the following functions.
1.It is used to stop the vehicle.
2.It is used to control the speed where and when required.
3.It is used to control the vehicle while descending along the slope.
4.To park the vehicle and held it in stationary position without the presence of
Driver.
Requirements of Automobile Brakes:
1.It should work efficiently irrespective of road condition and quality.
2.The retardation must be uniform throughout its application.
3.The pedal effort must be within the convenient capacity of the driver.
4.It must be reliable and should not be effected by heat water and dust.
5.It should be in minimum weight.
6.It should have long life.
7.It should be easy to maintain and adjust.
8.Noise and vibrations are to be minimum.
9.There should be provision for secondary brake or parking brake.
Stopping distance and Braking efficiency:
For practical measure for braking efficiency that of the minimum
distance in which it can be brought in to rest after the brake is applied.
The stopping distance depends upon
1.Grip between the tyre and road surface.
2.Tyre tread condition.
3.Tyre inflation.
4.Nature of road surface.
The stopping distance is calculated by
D=kv2
Where d=stopping distance in kilometers.
K=Constant depending upon the road and tyre inflation.
V=velocity of the vehicle per hour.
The value of k is 1/25 for 4 wheel braking system.
1/12 for 2 wheel braking system.
The braking efficiency is calculated by the equation:
η=V
2
/3D where v=velocity of the vehicle
d=stopping distance.
Condition of Brake Braking efficiency in %
1.Perfect 90%
2.Excellent 77%
3.Good 70%
4.Fair 60%
5.Poor 50%
6.Bad 37%
7.Very bad 30%
Below Fair is very danger.
Classification of Brakes: The following are the classifications of Brakes:
1.By method of power
a) Mechanical brakes
b) Hydraulic brakes
c) Vacuum brakes
d) Air brakes
e) Electrical brakes
f) Magnetic brakes
g) Air assisted hydraulic brakes
2.By method of application:
a) Service or foot brakes
b)Parking or hand brakes
3.By method of operation:
a) Manual
b) Servo
c) Power operation
4. By method of Braking contact
a. Internal Expanding Brakes
b. External Contracting Brakes.
5. By Method of Applying Brake force:
a. Single Acting Brakes.
b. Double Acting Brakes.
Types of Mechanical Brakes:
a. Drum Brakes (Internal Expanding or External Contracting)
b. Disc Brakes (Single or Two caliper)
Drum Brakes:
Construction: The main components of drum brakes are
1. Brake drum
2. Back plate
3. Brake shoes
4. Brake Liners
5. Retaining Springs
6. Cam
7. Brake Linkages
In this system the wheel is attached to drum. There are brake shoes used tocontact the rotating drum for braking operation. The shoes provide lining ontheir outer surface. The cam is used to lift the brake shoes at one end, otherend is connected by some method so as to make as the brake sleeve comeinto contact in the brake drum. The retaining spring is provided for bringingthe brake shoes back to its original position, after releasing the brake pedal.All these parts are fitted in the back plate and enclosed with brake drum. 
Working: When the pedal is pressed the cam moves the shoes outwardsthrough linkages, there by coming in frictional contact with the rotating drum.As soon as the brake pedal is released the retaining springs help the brakeshoes to brought back and release the brakes.
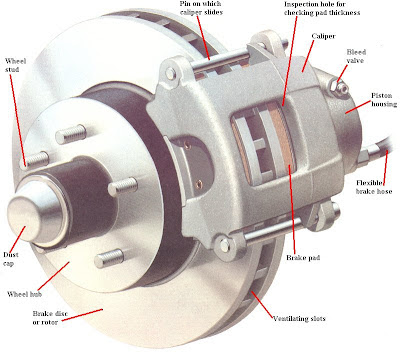
2. Disc brakes:
There are two types of disc brakes:
1. Spot Type
a. Swinging Caliper Type
b. Sliding caliper type
2. Clutch Type
Construction: The discs are made of gray cast Iron. The brake pressure in case of disc brakes have to be much lighter than the drum brakes. It consists of rotating disc and two friction pads which are actuated bythe four hydraulic wheel pistons contain in two halves of an assembly is calleda caliper. The caliper assembly is secured to the steering knuckle in a frontwheel brakes. The road wheel is fashioned to the outer surface of the disc.The friction pads rides freely on each side of the discs. They are in positionbeing the hydraulic systems.
Working:
When the brakes is applied hydraulic pressure is supply to the fluid inlettube, due to which the wheel cylinder piston force the friction pads againstthe rotating disc. In the released piston, the spring hold the piston pads sothat they maintain contact with disc surface.Construction and Working of Hydraulic systems: Hydraulic brakes make used of hydraulic pressure to force brake shoesout words against the brake drum based on PASCAL’S LAW.
1. Master Cylinder 2. Wheel Cylinder
The figure shows the master cylinder is connected by tubing to thewheel cylinder, at each of the four wheels. The system is filled with the liquidunder light pressure when the brake is not in operation. The brake fluidgenerally a mixture of glycerin and alcohol or caster oil, denatured alcoholand some additives. The brakes shoes which are mounted on the inner side of the brakedrum and do not rotate.
The brake liners are fitted on the outer surface of the brake shoes. The brake pedal is connected to the master cylinder piston bymeans of a piston rod.Working: When the brake pedal is pressed the piston is forced in to themaster cylinder, the hydraulic pressure is applied equally to all wheelcylinders. The pistons in the wheel cylinders pushed outwards against thebrake drum. When the driver release the brake pedal, the piston in the mastercylinder returns back to its original position due to the return spring pressure.Thus the pistons in the wheel cylinder come back in its original inward position.Thus the brakes are releasedConstruction and working of Master Cylinder
Master Cylinder: The Master Cylinder is the heart of the hydraulic brakesystem. It consists of two main chambers. The fluid reservoir which containsthe fluid to supply to the brake system, and the compression chamber inwhich the piston operates. The reservoir supplies fluid to the brake systemthrough two ports. The larger port is called the filler or intake part and isconnected to the hollow portion of the piston between the primary andsecondary cups which act as piston seals. The smaller port is called the relief,bypass or compensating port which connects the reservoir directly with thecylinder and lines when the piston is in the released position. When the brake pedal is depressed, the master cylinder piston movesforward to force the liquid under pressure into the system. The relief port issealed out of the system. The liquid pressure is conducted to the wheelcylinders, where it forces the wheel cylinder pistons out wards. These pistonsforce the brake shoes out against the brake drums When brake pedal is released, the return spring quickly forces the master cylinder piston back against the piston stop. Because the fluid in thelines returns rather slowly, a vacuum tends to form in the cylinder in front ofthe piston. This causes the primary cup to collapse to allow the liquid to flowfrom the reservoir through the filter port past the piston to fill the vacuum.Construction and working of Wheel Cylinder
WHEEL CYLINDER: Wheel cylinder is the second important hydraulic brakesystem. It consists of two pistons which can move in opposite directions by thefluid pressure. It is rigidly mounted on the brake shield or backing plate. Theboots protect the cylinders from foreign substances. Bleeder valves areprovided in the cylinder to permit air and liquid to be pumped out of thesystem during of the bleeding operation . Piston cup fits tightly in the cylinder against each piston and seal themechanism against leakage of the brake fluid. A Spring serves to hold thecups against the piston when the pressure is decreased. When the brakes are applied the brake fluid enters the cylinder from abrake line connection inlet between the two pistons. It causes to force outthe two pistons in opposite directions. This motion is transmitted to the brakeshoe. Directly or through links force them against the brake drum, thusapplying the brake.Construction and working of Tandem master Cylinder In this master cylinder there are two pistons in the and hydraulicpressure developed in two chambers one for the front left, and rear rightbrakes and other for the front right and rear left brakes. In tandem master cylinder one cylinder operates the front brakes whilethe other cylinder operates the rear brakes.Construction and working of Air Brake System: The air brake system consists of two-stage air-compressor driven by thecrankshaft or gearbox shaft. It takes air from atmosphere, compresses it anddelivers to the air reservoir through un-loader valve. Where the pressure ofthe reservoir reaches the maximum degree, the un- loader valve opens to theatmosphere. Then the compressed air is directed in to the atmospheredirectly. Each of the four wheels fitted with brake chambers consists of adiaphragm, and which the air pressure is applied and pushes it. This forceoperates the cam actuating lever and applies the brake. Each of the brakechamber is connected to the brake pedal, and air filter is also fitted betweenthe brake valve and reservoir.Working: When the brake pedal is pushed the brake valve opens andcompressed air is allowed in to the brake chamber. The brake valve consistsof three passages.1. Air intake 2. Exhaust 3. Brake chamber When the brake pedal is pressed the exhaust passage will be closedand Air intake passage open and compressed air goes back to the chamber.During return stroke the exhaust passage opens while intake closes and usedair goes to the atmosphere. This system fitted with an emergency mechanicalbrake, which can be used when air supply fails the air brake system, which is called air assisted hydraulic braking system.
Advantages:
1. This system used in heavy vehicles because they are more powerful
than hydraulic or mechanical brakes.
2. It simplifies the chassis design
3. The compressed air is used for purposes like tyre inflation; for horn,
windscreen wiper etc.
Disadvantage:
If there is any leakage in passage the entire system will be fail.
Therefore sealing of air is very difficult.
keywords: illinois asbestos attorney, alabama lawyer mesothelioma, mesothelioma attorney, asbestos lawyer, mesothelioma lawyers, asbestos attorney, mesothelioma lawyer, asbestos cancer attorney, texas asbestos lawyer, illinois mesothelioma lawyer, mesothelioma attorneys, mesothelioma litigation, mesothelioma attorney texas, mesothelioma attorney houston, illinois mesothelioma attorney, texas mesothelioma attorney, new york mesothelioma lawyers, minnesota mesothelioma lawyer, atlanta asbestos attorneys, new york mesothelioma attorneys, pennsylvania mesothelioma lawyers, phoenix dui attorney, dui attorney phoenix, arizona dui attorneys, dui lawyer arizona, phoenix dui lawyers, dui attorney arizona, phoenix arizona dui lawyer, arizona dui attorney, arizona dwi attorney, phoenix dui lawyer, arizona dui lawyer, dui lawyer phoenix, arizona dui lawyers, dui lawyer scottsdale, scottsdale dui attorney, dui attorneys arizona, tempe dui lawyer, az dui attorney, dui attorney scottsdale, automobile, mechanical engineering, autocad training,auto insurance, car insurance, car insurance quote, insurance quotes, low cost insurance, cheap insurance, cheap car insurance, cheap auto insurance, car cheapest insurance, car insurance quotes, automobile insurance, auto insurance quote, cheap car insurance quote, discount auto insurance, car insurance online, insurance rates, car insurance online quote, cheapest car insurance, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet, ebay, free, hotels, hotel, travel, free travel, free hotels, free cars, free home, free insurance, free place, cheap travel, free internet